Yoga, an ancient practice originating in India, encompasses physical, mental, and spiritual disciplines aimed at achieving harmony between the mind and body. Over millennia, it has evolved into various forms and styles, each offering unique benefits. This comprehensive exploration delves into the history, philosophy, types, benefits, and modern adaptations of yoga, providing a holistic understanding of this timeless practice.
Historical Evolution of Yoga
The roots of yoga trace back to the Indus-Saraswati civilization around 2700 BCE, where seals and artifacts depict figures in yoga postures, indicating its early presence. The term “yoga” first appears in the Rigveda, dating to approximately 1500 BCE, emphasizing the control of breath and the unification of mind and body.
During the pre-classical period, the Upanishads expanded upon Vedic teachings, introducing meditation and mantra recitation as pathways to enlightenment. The Bhagavad Gita, a seminal text from this era, discusses various forms of yoga, including Karma Yoga (path of action), Bhakti Yoga (path of devotion), and Jnana Yoga (path of knowledge).
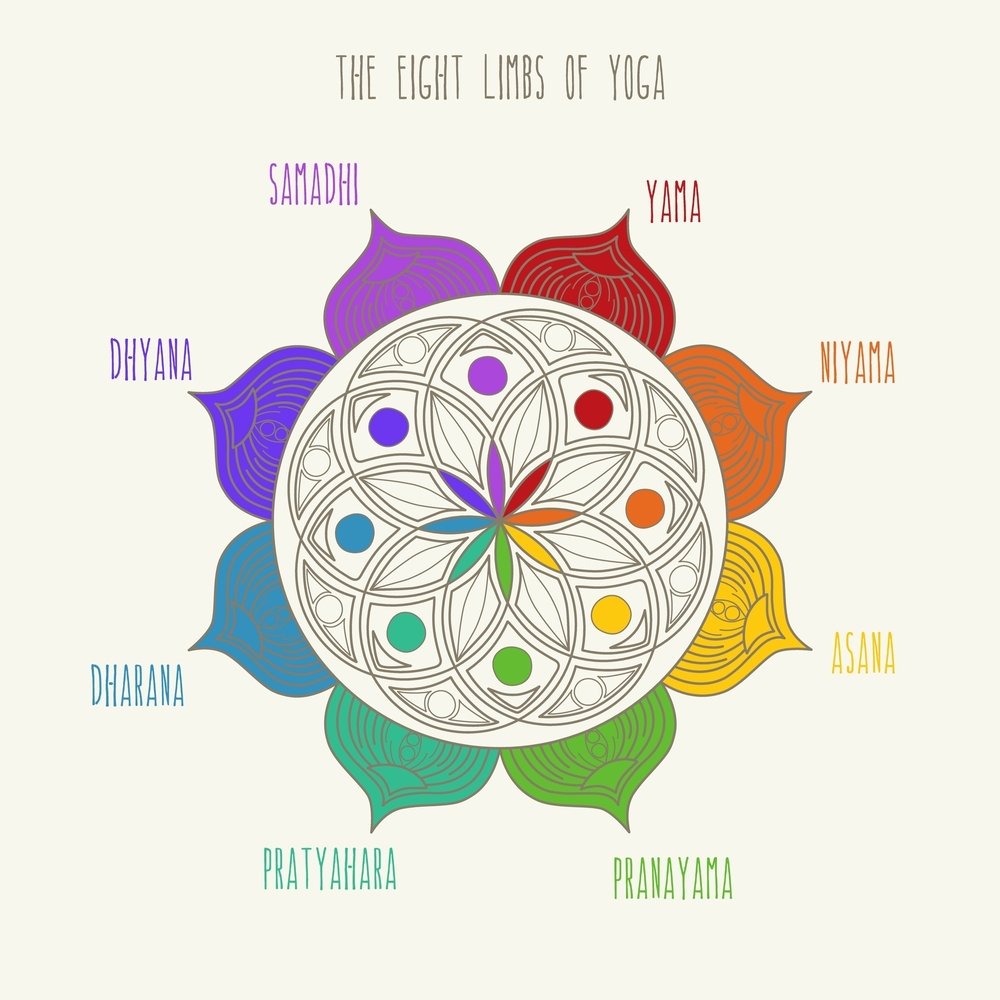
The classical period saw the systematization of yoga practices by Sage Patanjali, who compiled the Yoga Sutras, outlining the eight limbs of yoga (Ashtanga Yoga):
- Yama: Ethical restraints
- Niyama: Personal observances
- Asana: Physical postures
- Pranayama: Breath control
- Pratyahara: Withdrawal of senses
- Dharana: Concentration
- Dhyana: Meditation
- Samadhi: State of ecstasy or enlightenment
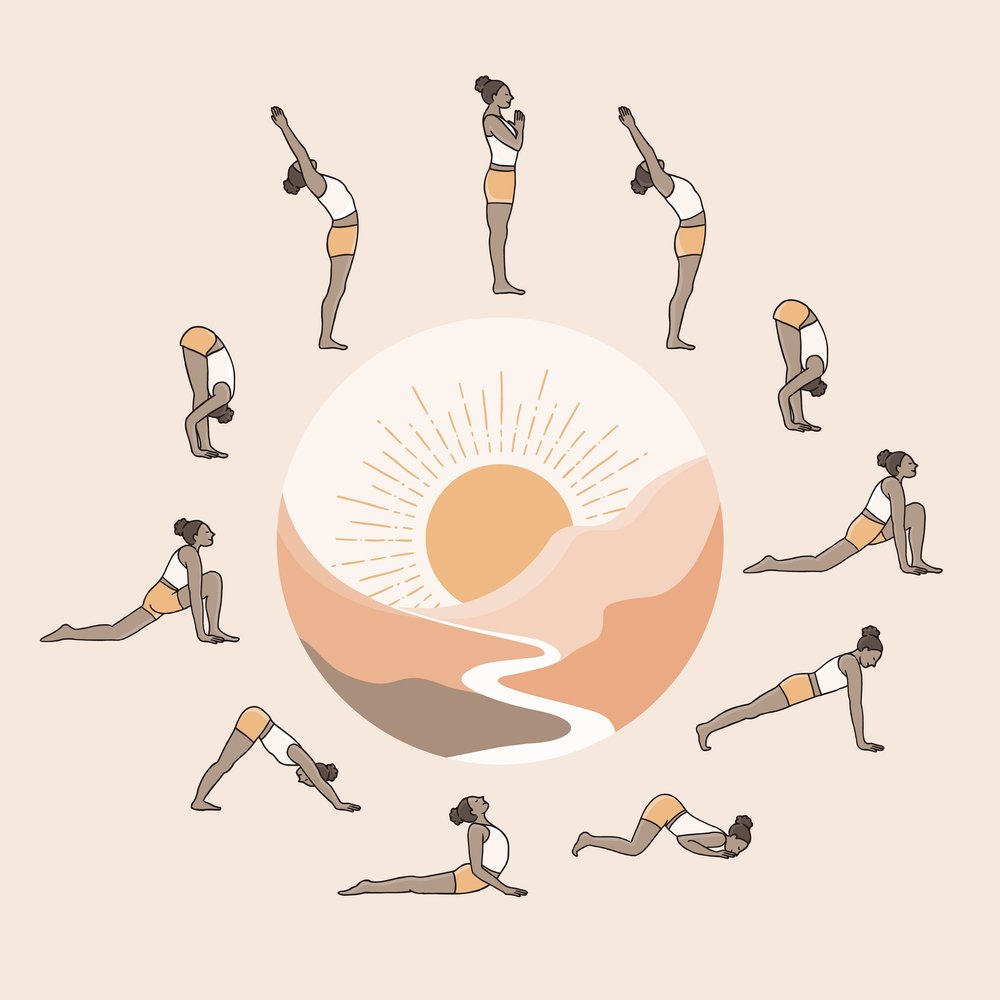
In the post-classical period, Hatha Yoga emerged, focusing on physical postures and breath control to prepare the body for meditation. This form laid the foundation for many modern yoga practices.
Philosophical Foundations
Yoga philosophy is deeply intertwined with the Samkhya school of thought, which posits a dualistic framework of consciousness (Purusha) and matter (Prakriti). Yoga aims to liberate the individual consciousness from the bindings of the material world, achieving a state of Kaivalya or ultimate freedom.
The Bhagavad Gita introduces the concept of equanimity, stating, “Samatvam Yoga Uchyate,” meaning equanimity in the mind is a sign of yoga. This underscores the importance of mental balance and detachment from the fruits of actions.
Types of Yoga
Yoga has diversified into various styles, each catering to different aspects of physical and mental well-being:
- Hatha Yoga: Emphasizes physical postures (asanas) and breath control (pranayama) to prepare the body for meditation.
- Raja Yoga: Focuses on meditation and strict adherence to the eight limbs outlined by Patanjali.
- Karma Yoga: The path of selfless action, encouraging practitioners to act without attachment to outcomes.
- Bhakti Yoga: Centers on devotion and love towards a personal deity, fostering a sense of unity with the divine.
- Jnana Yoga: Involves the pursuit of knowledge and wisdom, leading to self-realization.
- Ashtanga Yoga: A dynamic and physically demanding practice involving a set sequence of postures, synchronized with breath.
- Iyengar Yoga: Focuses on precise alignment and the use of props to aid in performing postures correctly.
- Vinyasa Yoga: Involves fluid transitions between postures, coordinated with breath, often referred to as “flow” yoga.
Benefits of Yoga
Scientific studies have highlighted numerous benefits of regular yoga practice:
- Improved Flexibility and Balance: Regular stretching and holding of postures enhance muscle elasticity and joint mobility.
- Stress Relief: Yoga reduces the secretion of cortisol, the primary stress hormone, promoting relaxation.
- Enhanced Mental Health: Practices like meditation and breath control alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Strength Building: Many postures require bearing one’s weight, strengthening muscles and bones.
- Cardiovascular Health: Yoga can lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Improved Sleep Quality: The calming effects of yoga help in falling asleep faster and achieving deeper sleep.
- Boosted Immunity: Yoga’s impact on reducing stress hormones strengthens the immune system.
Modern Adaptations and Global Spread
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, figures like Swami Vivekananda introduced yoga to the Western world, emphasizing its philosophical aspects. Over time, the physical components gained popularity, leading to the widespread practice of styles like Hatha and Vinyasa yoga globally.
Today, yoga is practiced worldwide, with variations catering to diverse populations. From therapeutic applications in healthcare settings to fitness-oriented classes in gyms, yoga’s adaptability has contributed to its global appeal.
Yoga Retreats: A Modern Sanctuary
The rise of yoga retreats offers practitioners an immersive experience to deepen their practice. Destinations like India and Ibiza have become renowned for retreats that blend traditional teachings with modern amenities. In India, retreats such as Ananda in the Himalayas and Vana integrate yoga with Ayurvedic and holistic therapies.
Ibiza, known for its vibrant nightlife, also offers serene yoga retreats. Six Senses Ibiza provides various yoga styles,